If shares are callable, the issuer can purchase them back at par value after a set date. If interest rates fall, for example, and the dividend yield does not have to be as high to be attractive, the company may call its shares and issue another series with a lower yield. Shares can continue to trade past their call date if the company does not exercise this option. The companies issuing shares of preferred stock can also realize some advantages. Within the spectrum of financial instruments, preferred stocks (or “preferreds”) occupy a unique place. Because of their characteristics, they straddle the line between stocks and bonds.
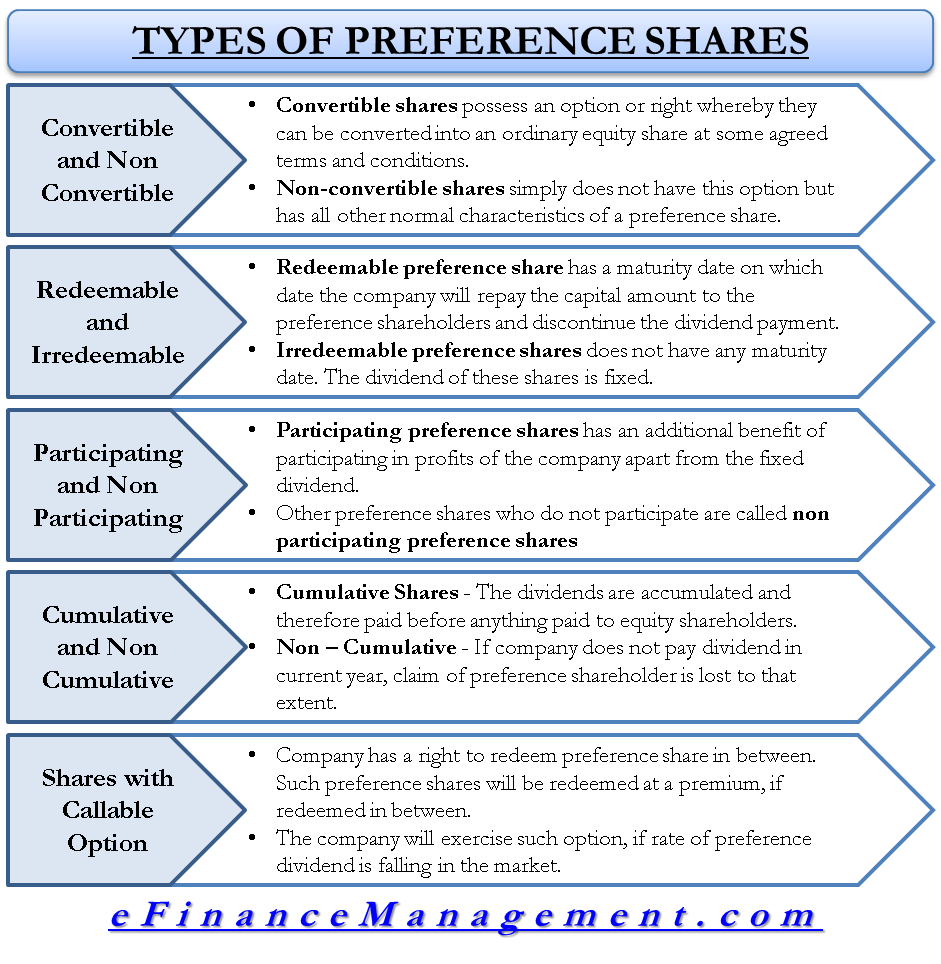
The Difference Between Preferred & Ordinary Shares
Investors should be aware of these potential pitfalls before incorporating preferred stock into their portfolios. Convertible preferred stock, in particular, allows investors to benefit from an increase in the value of the underlying common stock. The fixed dividend rate is usually expressed as a percentage of the stock’s par value, and it remains constant throughout the life of the stock. This preference ensures a certain level of stability in dividend payouts, making preferred stock an appealing option for income-oriented investors. Callable CPS is a type of CPS that can be redeemed by the issuer at a predetermined price and time. Callable CPS allows the issuer to redeem the stock if interest rates fall, which would allow the issuer to issue new CPS with a lower dividend rate.
- Preferred stockholders typically have no voting rights, whereas common stockholders do.
- With a variety of filtering criteria, you can screen for payment, maturity, call and convertibility features, and more.
- Delays or failure to pay accumulated dividends can damage investor confidence and credit worthiness.
- Whereas common stock is often called voting equity, preferred stocks usually have no voting rights.
- Should the preferred stock be purchased at a considerable discount to par value, there is more appreciation potential, but investors have to do the research to find these opportunities.
Compare With Other Investment Options
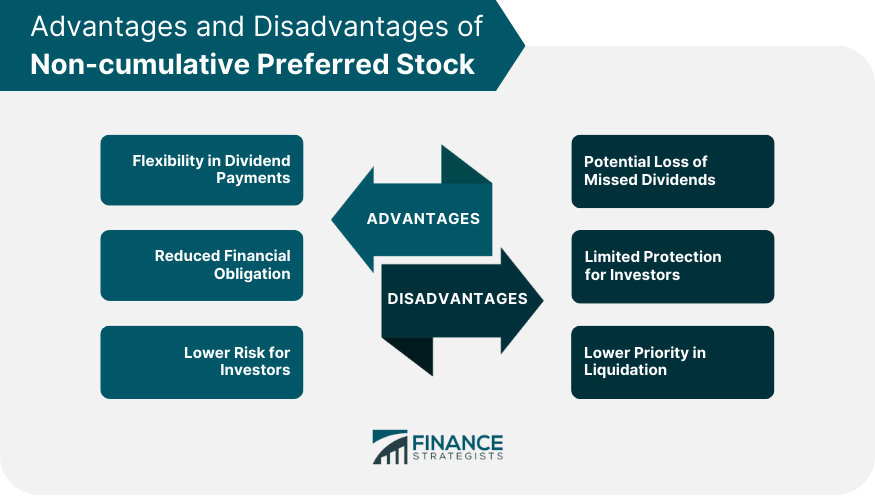
Non-cumulative preferred stock does not accumulate unpaid dividends; if dividends are not paid in a period, they are lost. Non-cumulative preferred stock offers greater flexibility to the company but carries higher risk for investors. It ensures that if dividends are not paid in a particular period, they accumulate and must be paid in the future. This feature can attract risk-averse investors who seek reliable dividend payments and a degree of security. CPS can be structured to be convertible into common stock at a predetermined price and time. This allows investors to participate in the potential capital appreciation of the company’s common stock while still receiving a fixed dividend rate.
Non-Cumulative Preferred Shares
As with convertible bonds, preferreds can often be converted into the common stock of the issuing company. This feature gives investors flexibility, allowing them to lock in the fixed return from the preferred dividends and, potentially, to participate in the capital appreciation of the common stock. what is cloud bookkeeping guarantees that if the company temporarily suspends dividend payments, the unpaid dividends accumulate and must be paid before dividends can be distributed to common shareholders. However, participatory shares guarantee additional dividends in the event that the issuing company meets certain financial goals. If the company has a particularly lucrative year and meets a predetermined profit target, holders of participatory shares receive dividend payments above the normal fixed rate. Like bonds, preferreds can help investors to preserve capital and generate income.
For preferreds, as they are both bond-and stock-like, their correlation profile is low relative to both asset classes, as shown below. Some types of preferred stock have a fixed end date in which, much like a bond, the original capital contributed is returned to shareholders. Preferred stock is a class of shares that give the holder a higher claim to dividends or asset distribution than common stockholders. While the fixed dividend rate provides a measure of stability, investors should still be prepared for some degree of price volatility.
Either of these may be different from the market price you paid for the preferred stock. For example, let’s say a company issues participating preferred shares at a dividend rate of $2.50 per share. Then, the company announces it will pay a dividend of $3.00 per share for common shares.
The exact terms of the “preference” that preferred shareholders’ get may vary from company to company. In some cases, the preference simply means that cash available for distributions during the year must be paid to preferred shareholders before common dividends are paid. In other cases, the preference means that any missed payments to preferred shareholders must be made up before common shareholders are allowed to receive anything. If the firm lacks the funds to pay preferred shareholders, its board of directors can suspend dividend payments indefinitely. This is a relatively drastic measure and would send a chilling message to all stakeholders.
This is in contrast to noncumulative preferred stock, which does not accumulate prior unpaid dividends. Unlike bondholders, failing to pay a dividend to preferred shareholders does not mean a company is in default. Because preferred shareholders do not enjoy the same guarantees as creditors, the ratings on preferred shares are generally lower than the same issuer’s bonds, with the yields being accordingly higher.
Preferred stock come in a wide variety of forms and are generally purchased through online stockbrokers by individual investors. The features described above are only the more common examples, and these are frequently combined in a number of ways. A company can issue preferred shares under almost any set of terms, assuming they don’t fall afoul of laws or regulations.


